Publications
2025
- Preprint
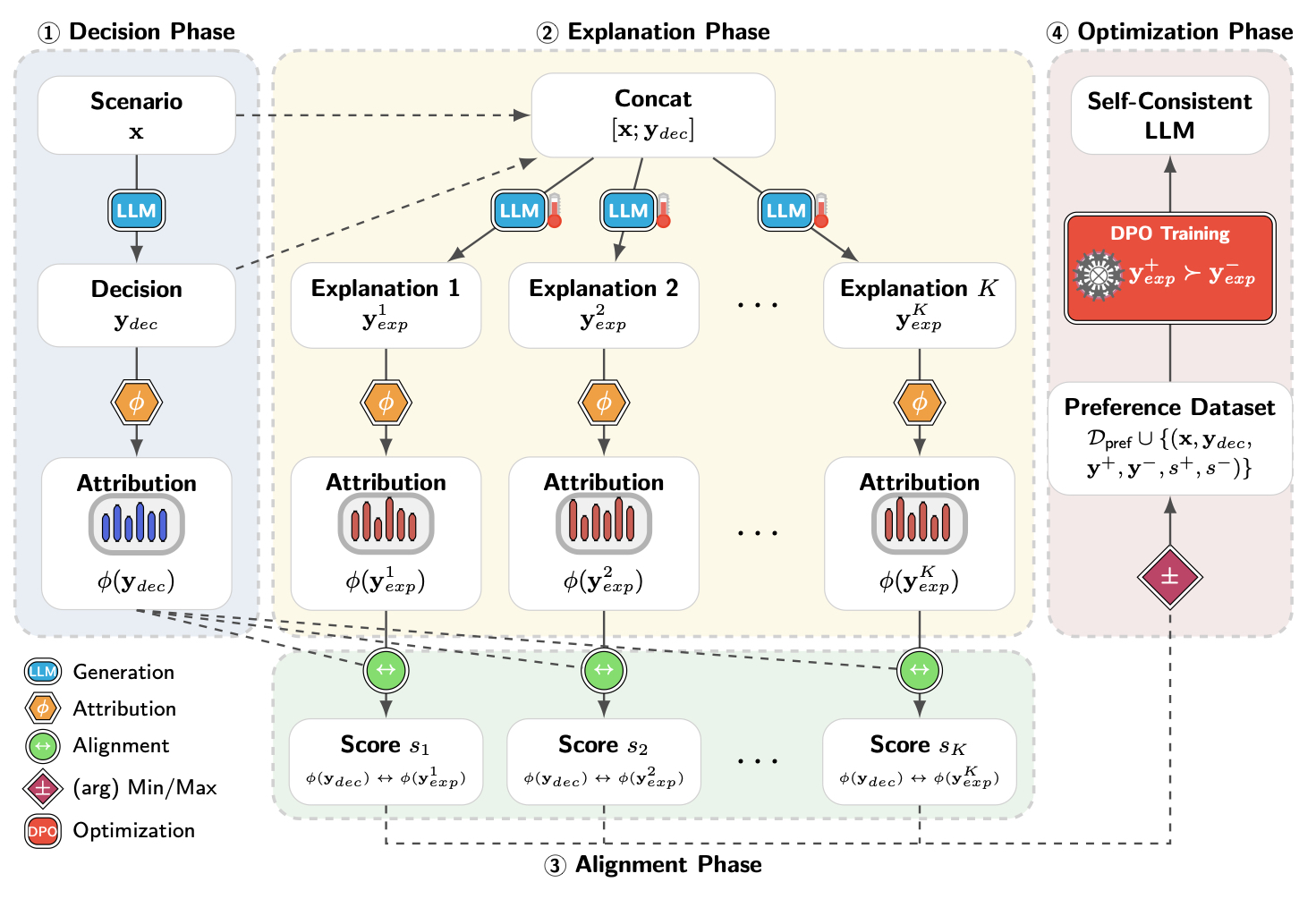 Towards Large Language Models with Self-Consistent Natural Language ExplanationsSahar Admoni, Ofra Amir, Assaf Hallak, and 1 more authorarXiv preprint arXiv:2506.07523, 2025
Towards Large Language Models with Self-Consistent Natural Language ExplanationsSahar Admoni, Ofra Amir, Assaf Hallak, and 1 more authorarXiv preprint arXiv:2506.07523, 2025Large language models (LLMs) seem to offer an easy path to interpretability: just ask them to explain their answers. Yet the features driving an answer often differ from those emphasized in its explanation, meaning post-hoc rationales can misrepresent what actually shaped the model’s output. We quantify this gap by comparing the feature-importance distributions of answers and their explanations. Prior analyses reveal such discrepancies, but large-scale study has been limited by the high computational cost of attribution methods. To address this, we introduce the Post-hoc Self-Consistency Bank (PSCB), a large-scale benchmark linking model decisions with diverse explanations and attribution vectors across datasets, methods, and model families. Using PSCB, we find that Spearman rank correlation provides a more reliable signal of alignment than cosine similarity. Building on this insight, we apply Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) to attribution-based preference data, improving alignment without degrading task accuracy. Our results pave the way toward scalable and faithful alignment between LLM decisions and their natural language explanations.
@article{admoni2025consistentency, title = {Towards Large Language Models with Self-Consistent Natural Language Explanations}, author = {Admoni, Sahar and Amir, Ofra and Hallak, Assaf and Ziser, Yftah}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2506.07523}, year = {2025}, } - Preprint
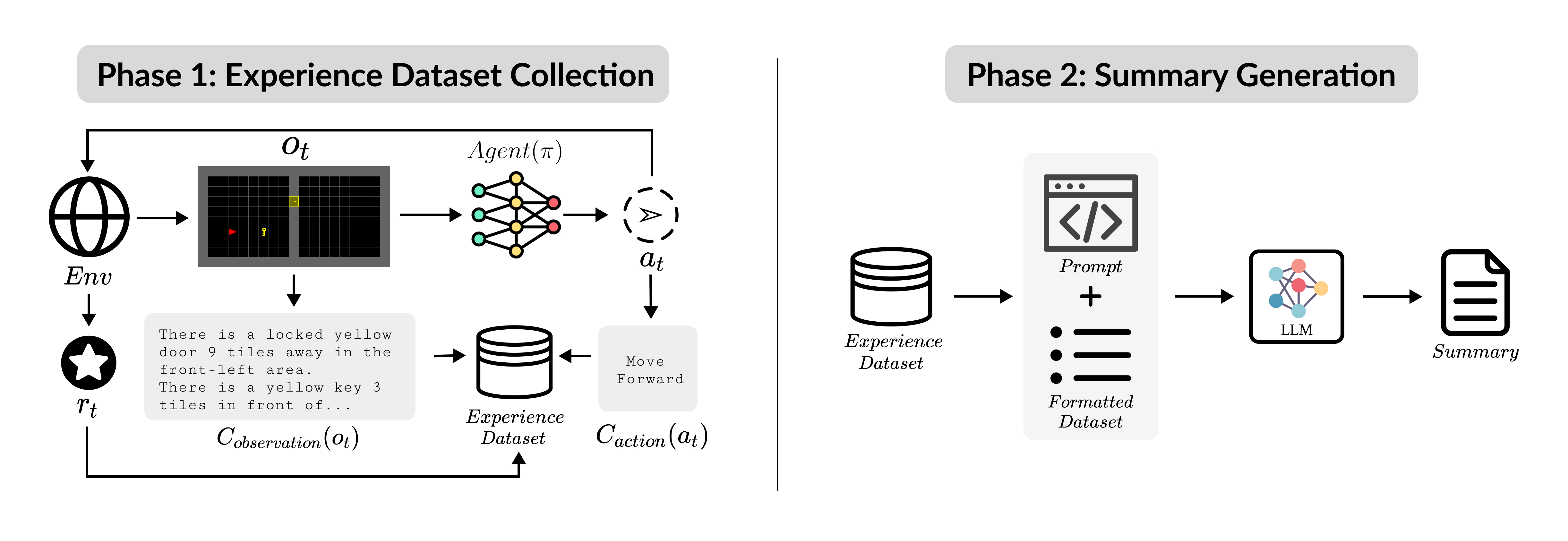 From Actions to Words: Towards Abstractive-Textual Policy Summarization in RLSahar Admoni, Assaf Hallak, Yftah Ziser, and 2 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2503.10509, 2025
From Actions to Words: Towards Abstractive-Textual Policy Summarization in RLSahar Admoni, Assaf Hallak, Yftah Ziser, and 2 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2503.10509, 2025Explaining reinforcement learning agents remains challenging, as policies emerge from complex reward structures and neural representations that are difficult for humans to interpret. Existing approaches rely on curated demonstrations that reveal local behaviors but offer limited insight into global strategy, leaving users to infer intent from raw observations. We propose \emphSySLLM (Synthesized Summary using Large Language Models), a framework that reformulates policy interpretation as a language-generation problem. Rather than relying on visual demonstrations, SySLLM translates spatiotemporal trajectories (an input modality outside the natural domain of LLMs) into structured text and prompts the model to produce coherent natural-language summaries that describe the agent’s goals, exploration style, and decision patterns. SySLLM scales to long-horizon and semantically rich environments without task-specific fine-tuning, leveraging the world knowledge and compositional reasoning of LLMs to capture latent behavioral structure across diverse agents. Expert evaluations show that SySLLM summaries align closely with human analyses of policy behavior, and in a large-scale user study, 75.5% of participants preferred these textual summaries over state-of-the-art demonstration-based explanations. Together, these results establish abstractive-textual summarization as a new, scalable paradigm for interpreting complex RL behaviors through language.
@article{admoni2025sysllm, title = {From Actions to Words: Towards Abstractive-Textual Policy Summarization in RL}, author = {Admoni, Sahar and Hallak, Assaf and Ziser, Yftah and Ben-Porat, Omer and Amir, Ofra}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.10509}, year = {2025}, }
2024
- CHI WorkshopTowards an evaluation of LLM-generated inspiration by developing and validating inspiration scaleHyungyu Shin, Seulgi Choi, Ji Yong Cho, and 6 more authorsIn Proceedings of the HEAL: Human-centered Evaluation and Auditing of Language Models CHI Workshop, 2024
Researchers seek inspiration during the research process. Large Language Models (LLMs) have the potential to inspire researchers to make progress in their research, especially in the ideation process, but it is challenging to assess this capability. We envision (1) developing a scale—Inspiration scale—that captures key elements of inspiration, (2) evaluating the capability of existing LLMs for inspiring researchers in the research ideation process, and (3) further transforming the developed scale into an auto-assessment rubric for LLMs to align human-perceived and machine-assessed inspiration. In this paper, we develop a list of items for human evaluators by (1) compiling metrics for inspiration through a systematic literature review and (2) contextualizing them in the context of research ideation. We discuss the next steps to validate our scale, evaluate LLMs using the scale, and develop an auto-assessment rubric aligned with our original scale.
@inproceedings{shin2024towards, title = {Towards an evaluation of LLM-generated inspiration by developing and validating inspiration scale}, author = {Shin, Hyungyu and Choi, Seulgi and Cho, Ji Yong and Admoni, Sahar and Lim, Hyunseung and Kim, Taewan and Hong, Hwajung and Lee, Moontae and Kim, Juho}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the HEAL: Human-centered Evaluation and Auditing of Language Models CHI Workshop}, year = {2024}, } - IJCAI WorkshopGenerating Global Policy Summaries for Reinforcement Learning Agents Using Large Language ModelsSahar Admoni and Ofra AmirIn Proceedings of the IJCAI Workshop on Explainable Artificial Intelligence, 2024
In this work, we present an initial exploration of generating global policy summaries for reinforcement learning (RL) agents using Large Language Models (LLMs). Prior work on explainable RL developed policy summary methods that aim to describe the behavior of agents to users by demonstrating their behavior in a subset of world-states. However, users can only watch a limited number of demonstrations, limiting their ability to understand the policy. Given the major advancements in LLMs and their ability to capture world knowledge, we hypothesize that they can be used to identify patterns of behavior based on a large dataset of agent interactions. We present a pipeline for generating natural language summaries and show a case study in a grid environment demonstrating the potential of the proposed approach.
@inproceedings{admoni2025globalsummary, title = {Generating Global Policy Summaries for Reinforcement Learning Agents Using Large Language Models}, author = {Admoni, Sahar and Amir, Ofra}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the IJCAI Workshop on Explainable Artificial Intelligence}, year = {2024}, }